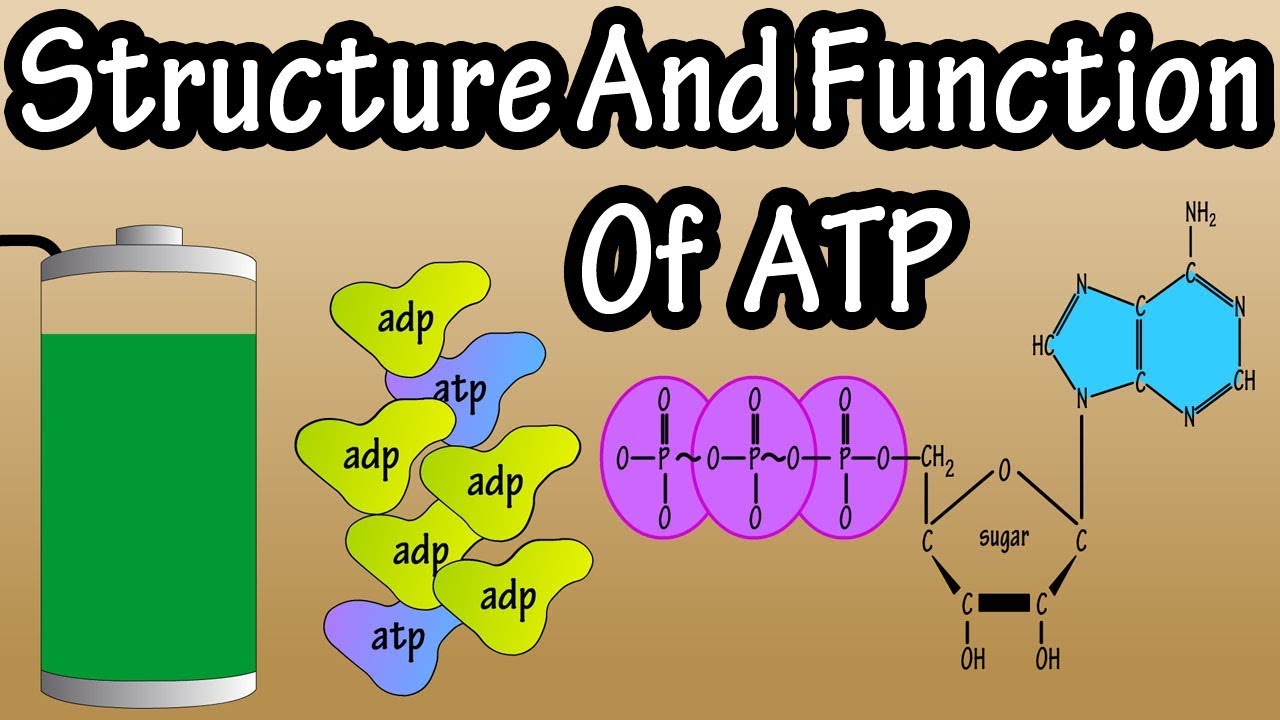
How are ATPs produced in the human body? ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the body's main energy currency. It is used to power all the cells in the body, from muscle contractions to nerve impulses. So, how is ATP produced? There are two main ways:
The first way is through cellular respiration. This is a process that uses oxygen to break down glucose, a type of sugar, into ATP. Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria of cells. The second way that ATP is produced is through glycolysis. This is a process that does not use oxygen and breaks down glucose into ATP. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of cells.
ATP is a vital molecule for life. Without it, our cells would not be able to function and we would quickly die. ATP is constantly being produced and broken down in the body, so it is important to have a steady supply of glucose to keep up with demand.
There are many ways to increase ATP production in the body. One way is to exercise regularly. Exercise helps to increase the number of mitochondria in cells, which in turn increases the capacity for cellular respiration. Another way to increase ATP production is to eat a healthy diet. A diet that is high in carbohydrates will provide the body with the glucose it needs to produce ATP.
How are ATPs produced in the human body?
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the body's main energy currency. It is used to power all the cells in the body, from muscle contractions to nerve impulses. Understanding how ATP is produced is crucial for comprehending the body's fundamental energy processes.
- Cellular respiration: The primary ATP production pathway, utilizing oxygen to break down glucose.
- Glycolysis: An alternative ATP production pathway, occurring without oxygen and breaking down glucose.
- Mitochondria: The cellular organelles responsible for cellular respiration and a significant site of ATP production.
- Glucose: The body's primary energy source, broken down to generate ATP.
- Exercise: A means to enhance ATP production by increasing mitochondrial count and cellular respiration capacity.
These key aspects are interconnected and essential for ATP production. Cellular respiration, occurring in mitochondria, is the major ATP producer, while glycolysis provides a backup pathway. Glucose serves as the fuel for both processes, and exercise promotes ATP production by increasing cellular respiration capacity. Understanding these aspects helps elucidate the body's energy production mechanisms.
Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells generate energy in the form of ATP. It is the primary ATP production pathway in the human body, utilizing oxygen to break down glucose, a type of sugar, into ATP. This process takes place in the mitochondria of cells.
- Components of cellular respiration: Cellular respiration involves three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of cells and breaks down glucose into pyruvate. The Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondria and further breaks down pyruvate into carbon dioxide and energy-carrier molecules. Oxidative phosphorylation also occurs in the mitochondria and uses the energy-carrier molecules from the Krebs cycle to produce ATP.
- Real-life examples of cellular respiration: Cellular respiration is essential for all life on Earth. It provides the energy that powers all cellular activities, from muscle contraction to nerve impulses. Without cellular respiration, our cells would not be able to function and we would quickly die.
- Implications of cellular respiration for ATP production: Cellular respiration is the most efficient way to produce ATP. It generates far more ATP than glycolysis, the alternative ATP production pathway. This is why cellular respiration is the primary ATP production pathway in the human body.
In conclusion, cellular respiration is the primary ATP production pathway in the human body. It is a complex process that involves the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen. This process generates far more ATP than glycolysis, the alternative ATP production pathway. Cellular respiration is essential for all life on Earth and provides the energy that powers all cellular activities.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is an alternative ATP production pathway that occurs without oxygen and breaks down glucose. It is the first stage of cellular respiration and takes place in the cytoplasm of cells. Glycolysis is less efficient than cellular respiration, but it is important because it can generate ATP without oxygen.
Glycolysis is important because it provides a backup ATP production pathway in case of oxygen deprivation. This can occur during exercise, when the body's demand for ATP exceeds the supply of oxygen. Glycolysis can also occur in cells that do not have mitochondria, such as red blood cells.
Understanding glycolysis is important because it helps us to understand how the body produces ATP. It also helps us to understand how the body can adapt to different conditions, such as exercise and oxygen deprivation.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are small organelles that are found in the cytoplasm of cells. They are responsible for producing ATP, the body's main energy currency. ATP is used to power all the cells in the body, from muscle contractions to nerve impulses. Without mitochondria, our cells would not be able to function and we would quickly die.
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells generate energy in the form of ATP. It takes place in the mitochondria of cells. The first stage of cellular respiration is glycolysis, which occurs in the cytoplasm. Glycolysis breaks down glucose, a type of sugar, into pyruvate. Pyruvate is then transported into the mitochondria, where it is further broken down in the Krebs cycle. The Krebs cycle generates energy-carrier molecules, which are then used in oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP.
Mitochondria are essential for ATP production. They are the only organelles that can perform oxidative phosphorylation, the most efficient way to produce ATP. Without mitochondria, the body would not be able to produce enough ATP to meet its energy needs.
Understanding the role of mitochondria in ATP production is important for understanding how the body functions. It also helps us to understand how diseases that affect mitochondria, such as mitochondrial disorders, can lead to a variety of health problems.
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar that is the body's primary energy source. It is broken down to generate ATP, the body's main energy currency. ATP is used to power all the cells in the body, from muscle contractions to nerve impulses. Without glucose, the body would not be able to function properly.
The process of breaking down glucose to generate ATP is called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria of cells. The first step in cellular respiration is glycolysis, which occurs in the cytoplasm of cells. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into two pyruvate molecules. Pyruvate is then transported into the mitochondria, where it is further broken down in the Krebs cycle. The Krebs cycle generates energy-carrier molecules, which are then used in oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP.
Glucose is essential for ATP production. It is the only molecule that can be used to generate ATP through cellular respiration. Without glucose, the body would not be able to produce enough ATP to meet its energy needs.
Understanding the connection between glucose and ATP production is important for understanding how the body functions. It also helps us to understand how diseases that affect glucose metabolism, such as diabetes, can lead to a variety of health problems.
Exercise
Exercise is a powerful way to enhance ATP production in the body. It does this by increasing the number of mitochondria in cells and the capacity of those mitochondria to produce ATP. This is important because ATP is the body's main energy currency, and it is used to power all the cells in the body, from muscle contractions to nerve impulses.
When you exercise, your muscles demand more energy. This increased demand for energy signals the body to produce more ATP. In response, the body increases the production of mitochondria in muscle cells. Mitochondria are the organelles that produce ATP, so by increasing the number of mitochondria, the body can increase its capacity to produce ATP.
In addition to increasing the number of mitochondria, exercise also increases the capacity of those mitochondria to produce ATP. This is because exercise helps to improve the efficiency of the Krebs cycle, which is the process by which mitochondria produce ATP. By increasing the efficiency of the Krebs cycle, exercise can help the body to produce more ATP with less effort.
The increased ATP production that results from exercise has a number of benefits. For example, it can help to improve muscle strength and endurance, reduce fatigue, and improve overall athletic performance. It can also help to improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes.
If you want to improve your ATP production, exercise is a great way to do it. Exercise is a safe and effective way to increase the number and capacity of mitochondria in your cells, which can lead to a number of health benefits.
FAQs on ATP Production in the Human Body
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the body's main energy currency. It is used to power all cellular activities, from muscle contractions to nerve impulses. Understanding how ATP is produced is crucial for comprehending fundamental bodily functions.
Question 1: How is ATP primarily produced in the body?
Answer: ATP is primarily produced through cellular respiration, a process that utilizes oxygen to break down glucose and generate ATP.
Question 2: What is the role of mitochondria in ATP production?
Answer: Mitochondria are the cellular organelles responsible for cellular respiration and are the primary site of ATP production in the body.
Question 3: How does exercise enhance ATP production?
Answer: Exercise increases the number of mitochondria in cells and enhances their capacity to produce ATP, leading to improved energy production.
Question 4: What is the significance of glucose in ATP production?
Answer: Glucose is the body's primary energy source, and it is broken down to generate ATP through cellular respiration.
Question 5: How does glycolysis contribute to ATP production?
Answer: Glycolysis is an alternative ATP production pathway that occurs without oxygen and breaks down glucose, providing a backup energy source.
Question 6: Why is understanding ATP production important?
Answer: Understanding ATP production is essential for comprehending cellular energy processes and how the body functions efficiently.
Summary: ATP production is a vital process in the human body, primarily occurring through cellular respiration in mitochondria. Glucose serves as the main energy source, and exercise enhances ATP production by increasing mitochondrial count and capacity. Glycolysis provides an alternative ATP production pathway. Comprehending ATP production is crucial for understanding cellular energy metabolism and overall bodily functions.
Transition to the next article section: This section explores the implications of ATP production for various bodily systems and discusses factors that can affect ATP levels.
Conclusion
ATP production is a fundamental process that underpins the functioning of all living organisms. In the human body, ATP is primarily produced through cellular respiration, a process that utilizes oxygen to break down glucose and generate ATP. This process takes place in the mitochondria of cells, which are the primary energy-producing organelles.
ATP is essential for all cellular activities, from muscle contractions to nerve impulses. Without ATP, our cells would not be able to function, and we would quickly die. Understanding how ATP is produced is crucial for comprehending fundamental bodily functions and the implications of various factors that can affect ATP levels.
H Pipe Vs. X Pipe: Which One Is Right For Your Muscle Car?
What Is A Closed System: A Comprehensive Guide
Mastering Reading Inference: Enhance Your Comprehension Skills

Cellular Respiration online presentation
ATPS 2021 AsiaPacific Focus on Fintech AiConnects.us
How Is Atp Used By The Body Wasfa Blog